Prototypes are called first editions in some cases. As the name suggests, a small number of samples are usually made based on product appearance drawings and structural drawings before mass production, so as to check product appearance or structural rationality and functional prototypes.
So which industries are the precise users of prototype factories or prototype companies? Using the big data tools of Webmaster Home, we search for prototypes
For this keyword, we found that the demand is relatively strong in industries such as automobiles, home appliances, electrical appliances, toys, medical equipment, technology, etc. To produce prototypes and rapid molds for these industries, commonly used domestic methods include: CNC processing, SLA, SLS, SLM, FDM, vacuum molding,
Low-pressure infusion and sheet metal production, we will compare these prototype processing methods in terms of definition, materials used, software used, machinable parts, advantages and disadvantages.
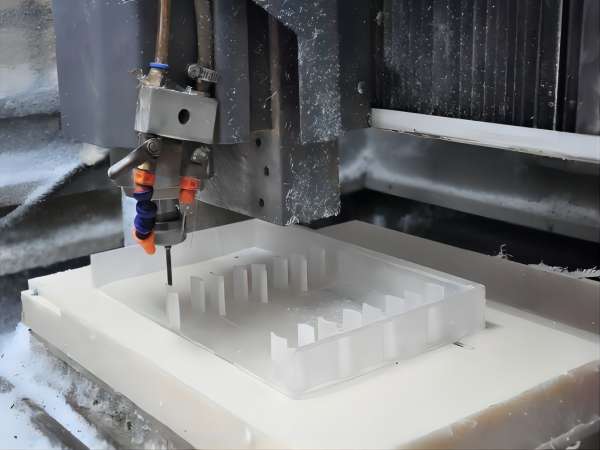
1. CNC machining
CNC machining is a computer numerical control machine tool that cuts a whole plate by controlling the tool path according to a programmed program. It is currently the most widely used prototype production method in China. The operation method is complicated and requires the operator to have rich experience.
It is mainly used for the processing of plastic and metal plates. It can be cut on all plates on the market. It is a material reduction technology that can only process fillets with a certain arc, but cannot directly process inner right angles. It must be processed through lines. Cutting / sparking and other processes to achieve.
2. SLA
SLA is stereolithography, a type of 3D printing technology. The materials used are mostly resins. Ultraviolet lasers of specific wavelengths and strengths are used to focus on the surface of the photosensitive resin to solidify it layer by layer. Finally, the layers are superimposed to form a three-dimensional entity. . All 3D printing is an additive technology, a process from 0 to 1.
SLA is the earliest rapid prototyping manufacturing process with high maturity. Prototypes are directly made from CAD digital models. The processing speed is fast and the product production cycle is short. There is no need for cutting tools and molds. It can process complex structural shapes or difficult to form using traditional means. Prototypes and molds.
SLA equipment is expensive and requires high factory environment. After molding, the strength, stiffness, and heat resistance are limited, which is not conducive to long-term storage.
3.SLS
SLS is selective laser melting, a type of 3D printing technology. The currently mature process materials are wax powder and plastic powder. When printing, the laser beam selectively sinters the tiled powder. After one layer is completed, the powder box is lowered, and another layer of powder is tiled for laser sintering. After all the powder is sintered, take out the powder box and remove the excess powder, and you can get a sintered part. .
The prototype mold made by SLS has high strength and good toughness, and can be used to make bearings, gears, precision components, and electronic components. Because it does not require support, the material utilization rate is high; but it is contaminated during the prototype processing process; the speed is relatively slow.
4.SLM
SLM, or selective laser melting molding technology, is currently the most common technology in metal 3D printing and molding. It uses finely focused light spots to quickly melt pre-set metal powder, directly obtaining parts of any shape and with complete metallurgical bonding, and the resulting production density can reach up to More than 99%.
In the process of making prototype molds with SLM, because the parts are usually complex, support materials need to be printed. After the parts are completed, the supports need to be removed and the surface of the parts needs to be processed, so the production time will be longer and the cost will be higher.
5.FDM
FDM is the fusion deposition molding method. The materials of FDM are generally thermoplastic materials, such as wax, ABS, nylon, etc., and are supplied in filament form. The material is heated and melted inside the nozzle. The nozzle moves along the cross-sectional contour and filling trajectory of the part while extruding the molten material. The material solidifies rapidly and condenses with the surrounding materials. In the process of making prototype molds with FDM, the price is relatively low, the materials are safe and harmless, and there is no mold fee. It can produce a variety of colors, but it cannot print hollow products. The prototype mold processed by FDM has obvious stripes, and the molding accuracy is relatively low. It requires the design and production of support structures, and the molding time is long.
6. Vacuum replica mold
Vacuum replica molding is to use product prototypes (such as SLA or prototype processing) to make silicone molds in a vacuum state, and use PU materials to cast them in a vacuum state, thereby cloning the same replica as the product prototype. Vacuum lamination is currently the most commonly used prototype replication technology in the world; the technology can be used to change the material of product prototypes, assemble prototypes, or conduct small batch production of products to meet the needs of performance testing, marketing and delivery during the product development process. Inspection, approval and other requirements; by using different PU materials, rubber parts, transparent parts, high temperature resistant parts, etc. can be copied. Ordinary PU materials are brittle, have poor toughness and high temperature resistance.
7. Low pressure perfusion
Low-pressure infusion, also known as low-pressure reaction injection molding, is a new process used in the production of rapid molded products. After mixing two-component polyurethane materials, they are injected into the rapid mold under normal temperature and low pressure. Through the polymerization and exchange of materials, Chemical and physical processes such as bonding and curing form products.
The low-pressure infusion-generated prototype mold has the advantages of high efficiency, short production cycle, simple process, and low cost. It is suitable for small batch trial production in the product development process, as well as small batch production of cover parts with relatively simple structures and large thick-walled and non-woven parts. Production of products with uniform wall thickness.
8. Sheet metal production
Sheet metal production refers to the processing of metal plates such as steel plates, aluminum plates, copper plates, etc., including laser cutting, stamping, bending, etc. The significant characteristic of the raw materials for sheet metal processing is that the thickness of the same part is consistent.